Creation of the pneumoperitoneum. The pressure plateau is selected according to the size, age, and gender of the patient (6-8 mmHg for children, 10-14 mm Hg for adults). The flow limitation of the CO2 gas should be set at 1 ml/min.
Every laparoscopic procedure begins with the exploration of the abdominal cavity! Here, an acute purulent appendicitis is observed, which is inflamed and adherent to the anterior abdominal wall.
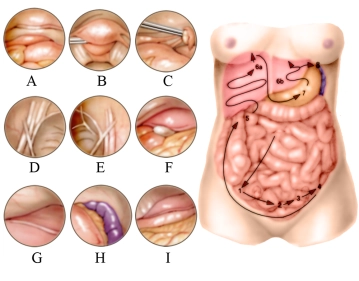
In the film, the right lower abdomen is first explored, followed by the right upper abdomen, then the left upper abdomen, the right lower quadrant again, and finally the small pelvis.
In relation to the sketch, the inspection of the lower abdominal organs occurs in numerical order, here after the inspection of the appendix area, uterus and bladder (A), the Douglas space (B), left ovary (C), and deep inguinal ring (D). It continues to the right over the right groin area (E). The optics are then directed to the right upper abdomen (5), inspection of the gallbladder (F) and right liver lobe (G). Further inspection of the left upper abdomen follows: spleen and stomach body (H) as well as the left liver lobe with falciform ligament, stomach, and greater omentum (I).