Hybrid-NOTES - Sigmaresektion - general and visceral surgery
You have not purchased a license - paywall is active: to the product selection
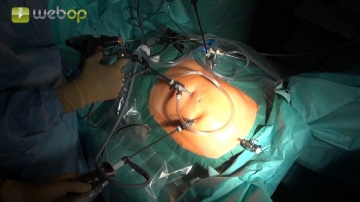
Establishing the pneumoperitoneum and placing the trocars
Establish the pneumoperitoneum via left subcostal puncture of the abdominal cavity with Veress needle.
Place the first trocar (5 mm) with a blunt obturator about 3 cm superior to the umbilicus. After gross inspection of the abdominal cavity, insert the other three 5 mm trocars under direct vision (5 mm laparoscope) into the left lateral and right mid-abdomen. Next, place the fourth trocar in the suprasymphyseal region.
Tip:
Infiltrate the skin with local anesthetic before each incision.
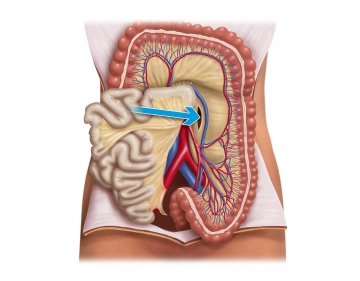
Dissecting on the Gerota fascia from medial and dividing the inferior mesenteric vein
Carefully incise the peritoneum medial to the inferior mesenteric vein and perform layer-by-layer, mainly blunt, medial to left lateral dissection of the mesocolon and descending colon from the Gerota fascia to the abdominal wall once the correct dissection layer has been identified.
Tip:
The small blood vessels should be left posteriorly when dissecting.
Caudal to the inferior aspect of the pancreas, repeatedly seal with “virtual clips” the inferior mesenteric vein along the newly created mesocolon edge centrally and peripherally and then transect. Next, dissect cranially directly along the peritoneum to reach the lesser sac anterior to the anterior surface of the pancreas without injury to its capsule. After splaying the bursa and the previously dissected cavity anterior to the Gerota fascia, carefully take down any adhesions to the pancreas in the direction of the left flexure.
Freeing the left colic flexure
Completely free the left flexure by detaching (in the proper plane) the greater omentum from the middle of the transverse colon to the left, thereby also opening the lesser sac. Then transect the splenocolic ligament and the last attachments between the pancreas and colon. Next, free the left colonic flexure from all posterior structures while sparing its mesocolon and thus its blood supply, which is a perquisite for a sufficiently long specimen and tension-free anastomosis.
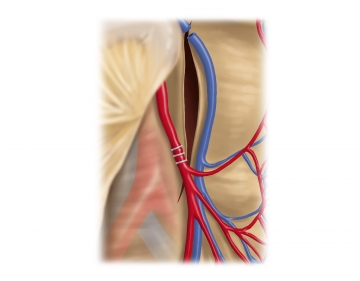
Dividing the inferior mesenteric artery
Now continue to free the descending mesocolon caudad and incise the peritoneum of the right mesosigmoid base to visualize, and clearly identify, the inferior mesenteric artery from posterior following mainly blunt dissection in the proper plane. Transect the artery away from its origin between clips with the Bowa sealing instrument while carefully sparing the hypogastric plexus.
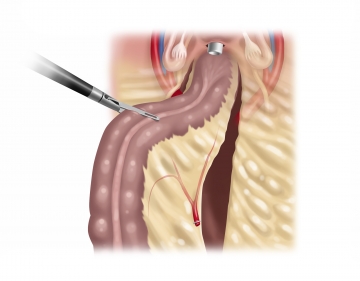
Detaching the colon from the lateral abdominal wall
Dissecting the proximal rectum
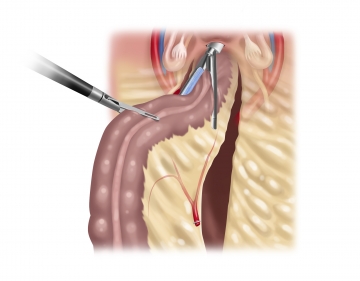
Transvaginal resection
Extracting the specimen
Closing the colpotomy
Preparing the anastomosis/purse string suture
Anastomosis
Colonoscopy, drainage
Single Access
Access to this lecture
for 3 days
€4.99 inclusive VAT

webop-Account Single
full access to all lectures
price per month
for the modul: vascular surgery