Skin incision about two or three finger breadths superior to the umbilicus; insert the Verres needle and establish pneumoperitoneum with 13mmHg under pressure control. Insert a 10mm shielded trocar Insert the laparoscope and explore the upper quadrants: There is an inflamed conglomerate mass; at its superior aspect the left hepatic lobe adheres to the diaphragm, while its inferior aspect is caked with the stomach and greater omentum.
-
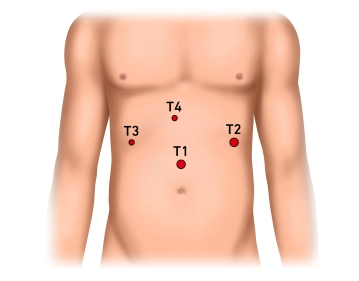
Establishing the pneumoperitoneum, inserting the trocar for laparoscope and exploring the upper quadrants
-
Inserting the working trocars, transecting the round and falciform ligaments of the liver
-
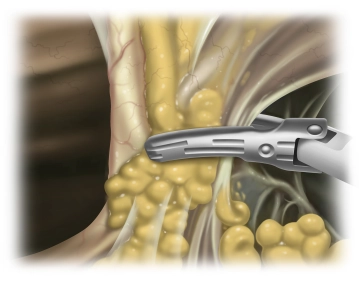
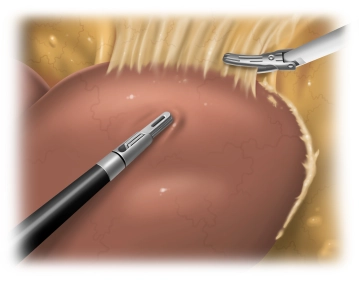
Freeing the liver
![Freeing the liver]()
Soundsettings Inflammatory changes make it rather difficult to free the left hepatic lobe. This requires freeing the liver step by step from adhesions with the diaphragm until the left hepatic vein has been freed. Due to extensive adhesions it is impossible to identify the triangular ligament as such. Both the stomach and the lesser omentum also display extensive adhesions with the visceral aspect of the left hepatic lobe. Detach the stomach from the inferior aspect of the liver, free the hepatic hilum and open up the lesser omentum all the way to the diaphragm.
Exchange the 12 mm trocar in the left upper quadrant against a 15 mm trocar for insertion of the ul
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$87.98/ yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$176.00 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.
... - Operations in general, visceral and transplant surgery, vascular surgery and thoracic surger
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$87.98/ yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$176.00 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.