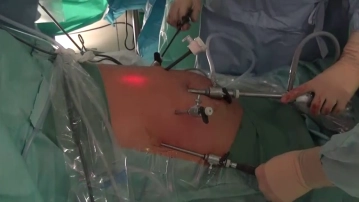
Through a transverse incision at the cranial umbilical pole, after creating the pneumoperitoneum, a 10mm optical trocar is inserted. Under transillumination, a total of four 5mm trocars are then placed semicircularly above the umbilical level, bilaterally at the midclavicular and anterior axillary lines. The surgeon operates through the two medial 5mm trocars, while the left liver retractor and the right gastric grasping forceps are introduced through the two lateral trocars. The patient is positioned in the anti-Trendelenburg position, and the operating table is slightly tilted to the left.
-
Accesses/Trocar Positions
-
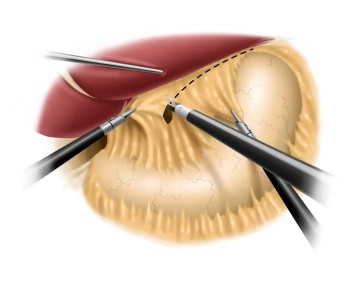
Incision of the lesser omentum and dissection of the right diaphragmatic crus
![Incision of the lesser omentum and dissection of the right diaphragmatic crus]()
Soundsettings The video clip can be played back with the automatic soundtrack of the subtitles.
In the sidebar registered users can enable and disable the automatic start of the dubbing.
Remark: Since this is a text-to-speech computer voice, it may mispronounce some medical terminology.Using a liver retractor, the left lobe of the liver is elevated, allowing a clear view of the esophageal hiatus. The preparation phase using an ultrasonic dissector begins with the incision of the lesser omentum in the area of the pars flaccida while simultaneously pulling the stomach to the left up to the free edge of the right diaphragmatic crus. The dissection of the right diaphragmatic crus follows, with the gastroesophageal junction being carefully prepared while preserving the posterior vagus branch.
Remarks:
- During preparation in the area of the lesser curvature, attention should be paid to aberrant and accessory hepatic arteries that branch from the left gastric artery and represent a common normal variant (12%).
- Completely intramural vagus trunks can occur. They should not be exposed under any circumstances.
- Preparation of the triangular ligament between the left liver lobe and diaphragm is not recommended, as the liver lobe could fall into the surgical field and obstruct the view.
- Fraying of the musculature of the diaphragmatic crura must be avoided at all costs.
-
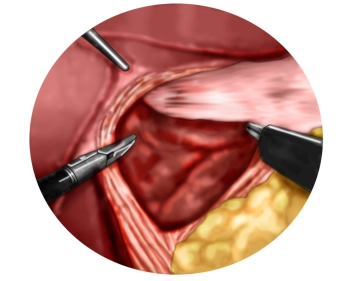
Dissection of the left diaphragmatic crus with entry into the mediastinum
![Dissection of the left diaphragmatic crus with entry into the mediastinum]()
Soundsettings The video clip can be played back with the automatic soundtrack of the subtitles.
In the sidebar registered users can enable and disable the automatic start of the dubbing.
Remark: Since this is a text-to-speech computer voice, it may mispronounce some medical terminology.One then proceeds anteriorly over the anterior commissure to the left diaphragmatic crus and also exposes it. In doing so, the mediastinum is opened ventrally.
Caution:
In this surgical step and in the further course, it is important to identify and preserve the anterior vagal branch.
-
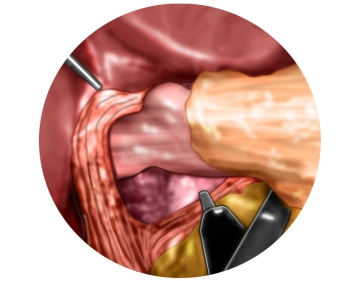
Mediastinal mobilization of the distal esophagus
![Mediastinal mobilization of the distal esophagus]()
Soundsettings The video clip can be played back with the automatic soundtrack of the subtitles.
In the sidebar registered users can enable and disable the automatic start of the dubbing.
Remark: Since this is a text-to-speech computer voice, it may mispronounce some medical terminology.Dissection is now carried far into the lower mediastinum, and the lower esophagus is circumferentially freed from its adhesions. During this process, the posterior vagus nerve is clearly identified and remains with the esophageal musculature. The dissection is significantly simplified by looping the esophagus, including the posterior vagus nerve, with a plastic loop. The esophagus is freed from the mediastinum to the extent that approximately 4-5 cm of the esophagus lie tension-free intra-abdominally.
-
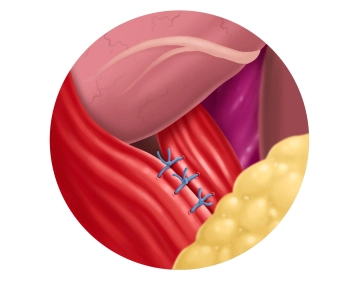
Posterior hiatus repair
![Posterior hiatus repair]()
Soundsettings The video clip can be played back with the automatic soundtrack of the subtitles.
In the sidebar registered users can enable and disable the automatic start of the dubbing.
Remark: Since this is a text-to-speech computer voice, it may mispronounce some medical terminology.To avoid constriction of the terminal esophagus by the subsequent hiatoplasty, a gastric tube Charrière (Ch) 40 is introduced transorally as a calibration bougie. The adaptation of the two diaphragmatic crura dorsal to the esophagus is performed using single button sutures, whose knots are tied extracorporeally and securely placed on site using a knot pusher ("Hangman knot"). Non-absorbable suture material of strength 0 is used. The clip demonstrates the first of a total of 3 sutures.
Tip:
- The sutures must include the peritoneal covering of the diaphragmatic crura, which is often displaced to the side during preparation.
- In very large hiatal hernias and in thoracic stomachs with a risk of volvulus, the hiatus can also be constricted anterior to the esophagus with sutures.
For the augmentation of the hiatus, a 6 × 8 cm resorbable mesh is cut in a keyhole shape and placed
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$87.34/ yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$174.70 / yearly payment
TachoSil® wird bei Erwachsenen und Kindern ab einem Alter von 1 Monat zur unterstützenden Behandlun
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$87.34/ yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$174.70 / yearly payment