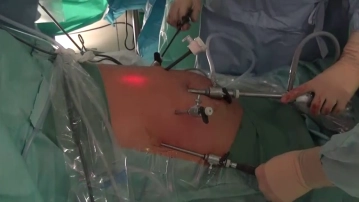
Through a transverse incision at the cranial umbilical pole, after creating the pneumoperitoneum, a 10mm optical trocar is inserted. Under transillumination, a total of four 5mm trocars are then placed semicircularly above the umbilical level, bilaterally at the midclavicular and anterior axillary lines. The surgeon operates through the two medial 5mm trocars, while the left liver retractor and the right gastric grasping forceps are introduced through the two lateral trocars. The patient is positioned in the anti-Trendelenburg position, and the operating table is slightly tilted to the left.
-
Accesses/Trocar Positions
-
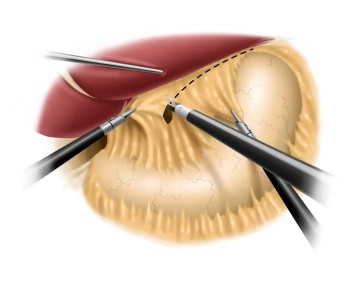
Incision of the lesser omentum and dissection of the right diaphragmatic crus
![Incision of the lesser omentum and dissection of the right diaphragmatic crus]()
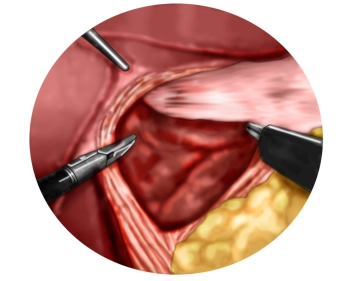
Soundsettings Using a liver retractor, the left lobe of the liver is elevated, allowing a clear view of the esophageal hiatus. The preparation phase using an ultrasonic dissector begins with the incision of the lesser omentum in the area of the pars flaccida while simultaneously pulling the stomach to the left up to the free edge of the right diaphragmatic crus. The dissection of the right diaphragmatic crus follows, with the gastroesophageal junction being carefully prepared while preserving the posterior vagus branch.
Remarks:
- During preparation in the area of the lesser curvature, attention should be paid to aberrant and accessory hepatic arteries that branch from the left gastric artery and represent a common normal variant (12%).
- Completely intramural vagus trunks can occur. They should not be exposed under any circumstances.
- Preparation of the triangular ligament between the left liver lobe and diaphragm is not recommended, as the liver lobe could fall into the surgical field and obstruct the view.
- Fraying of the musculature of the diaphragmatic crura must be avoided at all costs.
-
Dissection of the left diaphragmatic crus with entry into the mediastinum
Dissection is now carried far into the lower mediastinum, and the lower esophagus is circumferentia
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$88.58/ yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$177.20 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.
TachoSil® is used in adults and children from 1 month of age as supportive treatment in surgery for
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$88.58/ yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$177.20 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.