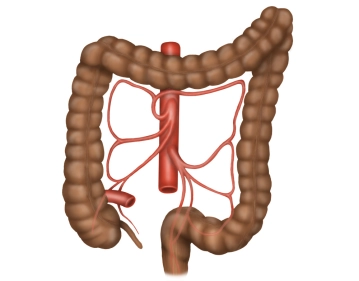
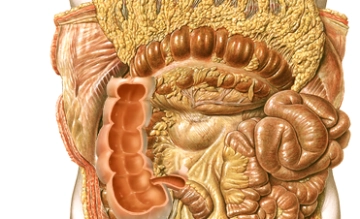
The colon encircles the inner abdominal wall and runs below the liver and stomach, surrounding the loops of the small intestine. The position of the colon is intra- or secondarily retroperitoneal. Its primary function is the thickening of the chyme by absorbing water. The total length of the colon is on average 120-150 cm. The colon begins at the ileocecal valve and ends at the rectosigmoid junction, where it transitions into the rectum.
The colon is divided into the following sections:
- Cecum with the appendix
- Ascending colon
- Transverse colon
- Descending colon
- Sigmoid colon