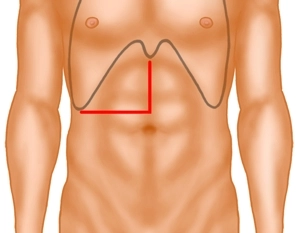
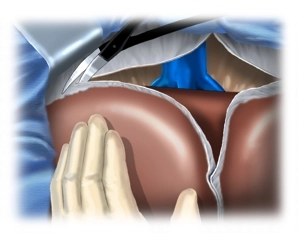
The laparotomy is performed via a median incision with extension into the right flank, whereby the incision deviates just above the navel into the right flank. Then transection of the right-sided rectus musculature using bipolar scissors and opening of the peritoneum. The incision can be carried past the xiphoid on the left: This gains an additional good stretch, which facilitates the view, especially to the hepatic veins.
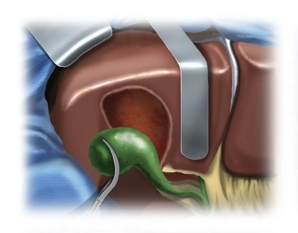
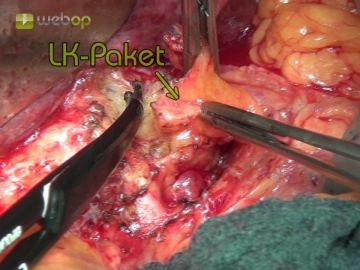
Subsequently, the falciform ligament of the liver is detached close to the abdominal wall. After folding back the wound edges, insertion of the abdominal wall retractor and inspection of the situs: Exclusion of extrahepatic metastases or conspicuously large lymph nodes in the hilus in primary liver carcinomas; in the shown case, there is liver cirrhosis.
Note:
Small interventions on the left liver lobe up to left-lateral resections can also be performed via a median laparotomy, wedge excisions from the inferior segments IVb, V and VI via a subcostal incision.