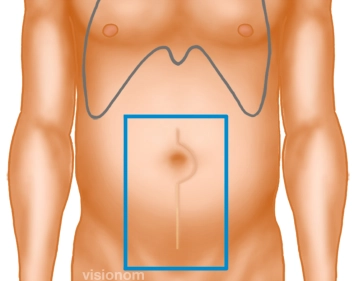
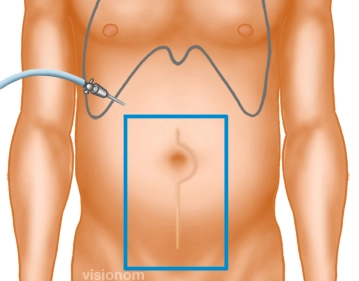
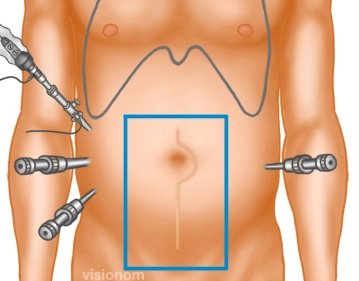
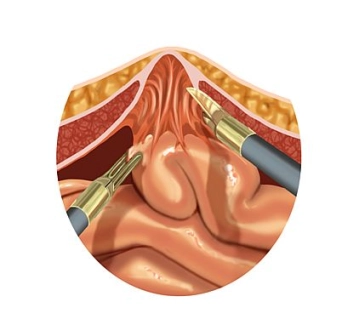
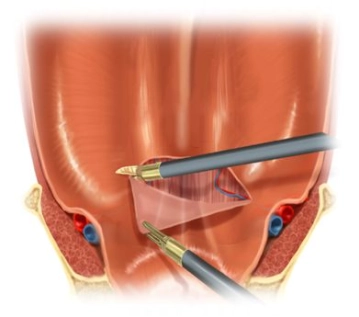
Before establishing the pneumoperitoneum, the edge of the scar plus sufficient overlap is traced in all directions, thereby determining the size of the mesh.
Since in this case the fascia defect extends mostly to the right, the mesh must be placed asymmetrically.