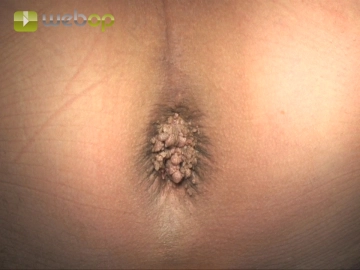
Expose the lesions and confirm diagnosis by sending specimen for histopathology. The easiest way to do this is through excision with scissors. All suspected malignant lesions must be studied separately.
-
Assessment of finding; specimen for histopathology
-
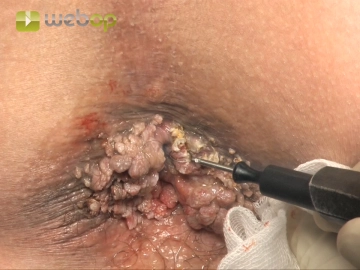
Snare excision
![Snare excision]()
Soundsettings Remove all lesions as small as possible and always in completely superficial epicutaneous fashion. Here, too, the wet-resection technique can be recommended, as it improves the conduction of the current and better protects the environment through cooling. The excision must not involve the entire skin. This is unnecessary, since without exception the location of each lesion is epicutaneous. If a lesion extends more deeply, infiltrative growth may be present, in which case a more extensive and deeper excision becomes necessary (see AIN and anal cancer).
Once again with wet-resection technique destroy each lesion with electric current and then complete
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$87.98/ yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$176.00 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.