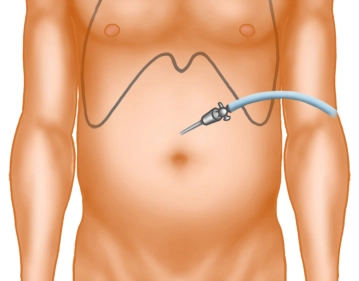
A small skin incision is made well above the navel in the midline. After inserting the Veress needle and verifying the correct position, the pneumoperitoneum is established.
-
Skin incision
-
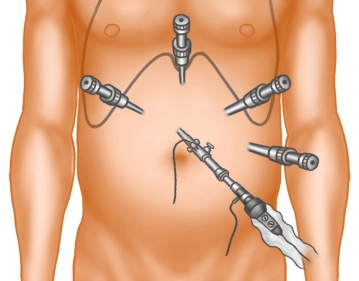
Trocar positioning
-
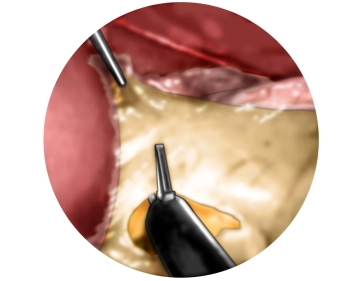
Traction of the stomach and incision of the lesser omentum
-
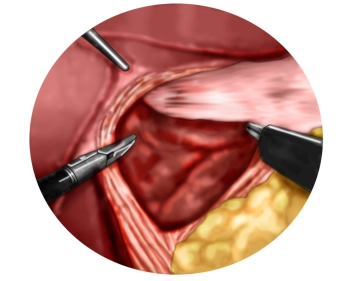
Preparation of the diaphragmatic crura with entry into the mediastinum
Preparation of the lower esophagus
One now proceeds far into the lower mediastinum and circumferentially mobilizes the lower esophagus
One now proceeds far into the lower mediastinum and circumferentially mobilizes the lower esophagus
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
US$9.40
inclusive VAT
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
from US$7.33 / module
US$87.98/ yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$14.66
/ month
US$176.00 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.