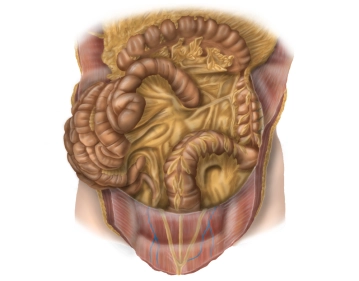
The following parts of the intestine are relevant during the operation:
- Descending colon:
- Location: secondary retroperitoneal
- Peritoneal suspension: fused with the posterior wall of the abdominal cavity
- Course: from the left flexure (here: phrenocolic ligament with fixation to the spleen) to the iliac fossa, connects to the transverse colon and transitions into the sigmoid colon
- Length: 20-30 cm
- Sigmoid:
- Location: intraperitoneal
- Peritoneal suspension: sigmoid mesocolon
- Course: from the iliac fossa as a loop (S-shaped) to the level of the 2nd-3rd sacral vertebra, connects to the descending colon and transitions into the rectum
- Length: variable (elongated sigmoid), usually about 35 cm
- Rectum:
- Transition from sigmoid colon to rectum before the 2nd-3rd sacral vertebra.
- Length 16 cm
- Division into thirds: The height of the margins is measured with a rigid endoscope, using the anal-cutaneous line as a reference.
- Lower third 0-6cm
- Middle third 6-12cm
- Upper third 12-16cm
- each measured from the anal-cutaneous line