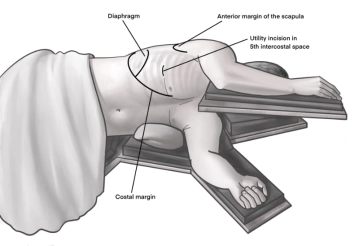
Incision of approximately 4 cm in length in the area of the anterior axillary line at the upper edge of the 5th rib to access the 4th intercostal space above. A helpful orientation is often an imaginary line from the tip of the scapula to the nipple. Transection of the subcutis on the rib with the monopolar knife. Subsequently, stepwise preparation of the intercostal muscles with the monopolar knife. The pleura is opened bluntly with a finger. Palpation of the thoracic wall for adhesions and insertion of a wound protection film.
-
Access uniportal VATS right
![Access uniportal VATS right]()
-
Preparation of the interlobium
![Preparation of the interlobium]()
Soundsettings First, the operation begins with the exposure of the interlobar part of the pulmonary artery. For this, the parenchymal bridge between the upper and middle lobes is prepared using an ultrasonic scalpel. A large lymph node from station 11 is retrieved in the process.
Tip: In anatomical resection, the sequence of surgical steps can vary depending on the intraoperative situation.
-
Dissection of the segmental artery A8
![Dissection of the segmental artery A8]()
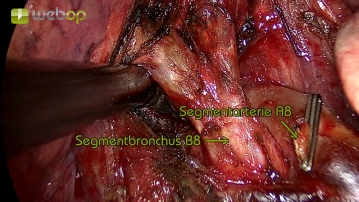
Soundsettings The circular presentation of the pars interlobaris of the pulmonary artery is performed. The depiction of the branches to the middle lobe (segmental arteries A4&A5) is omitted if the vessels clearly run into the lower lobe. The segmental artery A8 is now presented circularly and bluntly encircled. This is followed by traction using Vicryl ligature, placement of titanium clips, and dissection with the ultrasonic scissors.
-
Resection of the segmental bronchus B8
![Resection of the segmental bronchus B8]()
Soundsettings The bronchial system typically runs slightly offset from the branches of the pulmonary arteries. Therefore, after severing the segmental artery A8, the view of the segmental bronchus B8, here with an early division into the subsegments B8a and B8b, is clear. Blunt dissection is performed again until encircling and ligating with a Vicryl suture is possible. Then, a titanium clip is placed centrally, and sharp transection with scissors is performed to avoid thermal damage to the segmental bronchus stump.
After resecting the segmental bronchus, a lymph node from station 12 is visible at the angle of the
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$52.30/ yearly payment
thoracic
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$104.60 / yearly payment