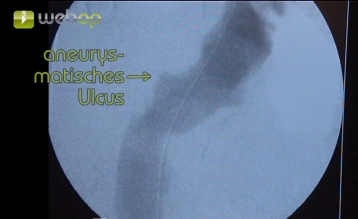
In the article, the endoluminal exclusion of a penetrating atheromatous ulcer (PAU, eccentric 32 x 24 mm) of the descending aorta is demonstrated. Due to two previous vascular surgical operations in the left groin and severe arteriosclerosis, an extraperitoneal exposure of the external iliac artery is performed.
For a diameter or depth of the ulcer of ≥ 20 mm, elective endovascular treatment is indicated. In cases of signs of impending rupture (pain, extra-aortic blood), endovascular treatment is urgent. Pain is mentioned as one of the main criteria for urgent surgical intervention.