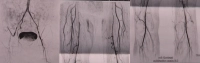
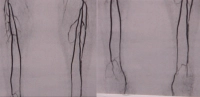
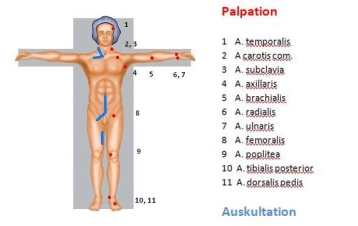
According to the TASC criteria, therapeutic treatment options can be derived depending on the local occlusion/stenosis length. The length of the stenosis and its localization regions determine the therapy: endovascular or open vascular surgery.
TASC criteria of aortoiliac vascular occlusions
Types | Morphology | Therapy principle |
|---|---|---|
A | Focal stenoses of the common iliac artery or external iliac artery <3 cm, uni- or bilateral | endovascular |
B | Focal stenoses 3–10 cm long and/or unilateral occlusion of the common iliac artery | endovascular |
C | Bilateral stenoses of the common iliac artery, 5–10 cm or unilateral complete occlusion of the external iliac artery or bilateral occlusions of the common iliac artery | open reconstruction |
D | Diffuse stenotic changes of the entire iliac axis or unilateral occlusion of the common and external iliac artery or bilateral occlusions of the external iliac artery | open reconstruction |
Video example: PAOD stage IIb right leg with subtotal stenosis of the external iliac artery, common femoral artery occlusion, profunda origin occlusion, long-segment occlusion of the superficial femoral artery, occlusion of the anterior tibial artery on both sides (right proximal, left peripheral) -> TASC D
Fontaine stage | Clinical presentation | Rutherford category | Grade | Clinical presentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
I | asymptomatic | 0 | 0 | asymptomatic |
IIa | Walking distance > 200 m | 1 | I | mild intermittent claudication |
IIb | Walking distance < 200 m | 2 | I | moderate intermittent claudication |
| 3 | I | severe intermittent claudication | |
III | ischemic rest pain | 4 | II | ischemic rest pain |
IV | Ulcer, gangrene | 5 | III | minor tissue loss |
6 | III | major tissue loss |