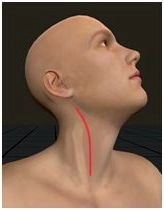
After infiltration anesthesia incise the skin along the medial border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Transect the subcutis and platysma, then enter the anterior fascia of the neck and open the vascular sheath. Ligate and divide the fascial vein.
-
Right cervical access
-
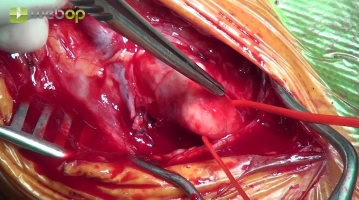
Dissecting the common carotid artery
Dissecting the internal and external carotid arteries
Carefully mobilize the ICA and ECA in no-touch technique and then encircle the ECA with a surgical
Carefully mobilize the ICA and ECA in no-touch technique and then encircle the ECA with a surgical
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
US$9.40
inclusive VAT
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
from US$4.37 / module
US$52.55/ yearly payment
vascular surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$8.75
/ month
US$105.10 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.