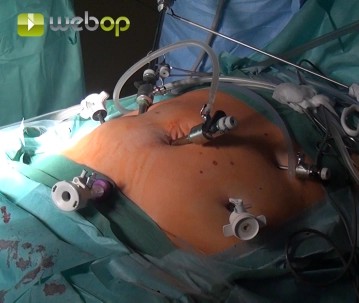
Due to obesity and a periumbilical scar, establish the pneumoperitoneum by inserting the Veress needle subcostally in the left epigastrium. First, by blunt scissor dissection fashion the channel for a 10mm trocar in the right mid-abdomen and insert the trocar. Now, under direct vision insert another 10 mm trocar at the umbilicus and a 5 mm trocar in the right lower quadrant. Through this 5 mm trocar clear the adhesions with the median umbilical ligament as far as the bladder while staying close to the abdominal wall. Then, insert a 12 mm trocar in the suprasymphyseal region of the planned Pfannenstiel incision. Insert another two 5 mm trocars in the left middle abdomen and left epigastrium, in the latter case at the site of the Veress needle.
-
Inserting the Veress needle and trocar placement
-
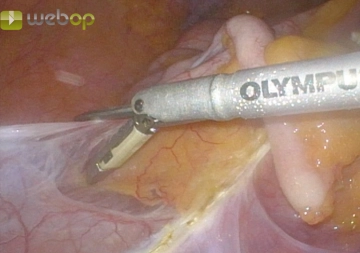
Dissecting the ileocecal junction
First, mobilize the terminal ileum, cecum, and ascending colon from inferior and laterally while sparing the Gerota fascia.
Note: While dissecting the right hemicolon, the surgeon and first assistant stand to the left of the patient facing the monitor on the patient's right side. From the time of dissecting the left hemicolon (step 7) until the end of the operation, the sides are switched, with a second monitor now positioned on the left side of the patient.
-
Mobilizing the ascending colon and taking down the hepatic flexure
On the Gerota fascia, fully mobilize the ascending colon with its mesenteric root up to the duodenum and expose the latter completely. Dissect the hepatic flexure laterally and superiorly and divide adhesions to the gallbladder and a double-barrel configuration between the ascending and transverse colon.
-
Taking down the greater omentum
-
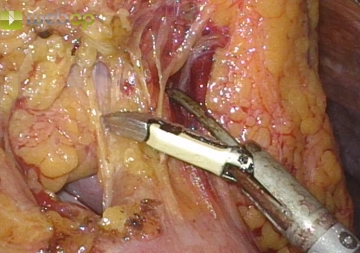
Dividing the ileocolic vessels
After having completely mobilized the distal ileum, divide the right mesocolon, step by step and cl
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
€44.50 / yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
€149.00 / yearly payment