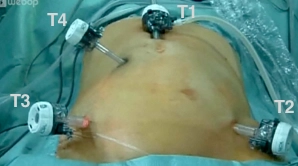
The skin is incised in the midline approximately 3 cm cranial to the navel, the camera trocar (T1) is introduced into the abdominal cavity via a mini-laparotomy, and the pneumoperitoneum is established. After an orienting inspection of the abdominal cavity, the working trocars (T3, T4, T2) are introduced under direct vision.
Note:
The risk of injury to major intra-abdominal vessels by using a Veress needle to establish the pneumoperitoneum must be considered.