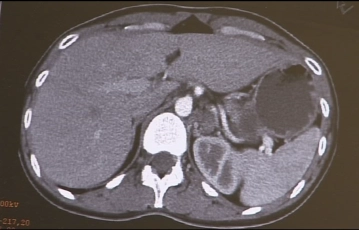
Imaging demonstrates a multinodular 5cm–6cm large cyst-like mass in the region of the left adrenal, clinically confirmed as pheochromocytoma.
-
CT findings
![CT findings]()
-
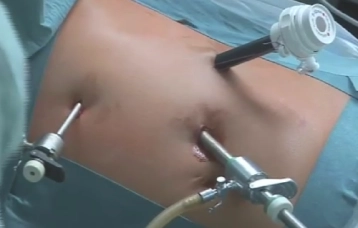
Trocar positioning
![Trocar positioning]()
Perform medial 2cm long minilaparotomy in left upper quadrant for the trocar of the laparoscope and then initiate pneumoperitoneum. After exploration of the abdominal cavity introduce two more working trocars – one 5mm trocar in the left upper quadrant and a Versa-Port V12 anterior to the 11thrib.
-
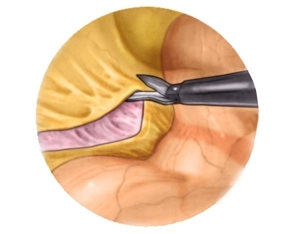
Freeing the descending colon
![Freeing the descending colon]()
Soundsettings The video clip can be played back with the automatic soundtrack of the subtitles.
In the sidebar registered users can enable and disable the automatic start of the dubbing.
Remark: Since this is a text-to-speech computer voice, it may mispronounce some medical terminology.Pull the descending colon mediad and incise the retroperitoneum in the avascular plane anterior to the left kidney.
-
Opening the prerenal space
![Opening the prerenal space]()
Soundsettings The video clip can be played back with the automatic soundtrack of the subtitles.
In the sidebar registered users can enable and disable the automatic start of the dubbing.
Remark: Since this is a text-to-speech computer voice, it may mispronounce some medical terminology.Approach the left adrenal laterally by freeing the left colic flexure step by step from the retroperitoneum until large parts of the anterior aspect of the Gerota fascia and renal capsule have been exposed.
Note:In slender patents it may become difficult to spare the Gerota fascia.
-
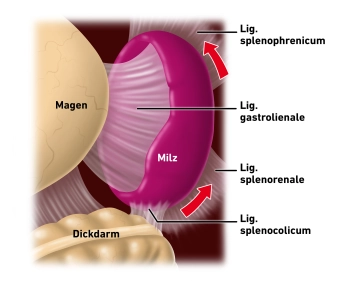
Dissecting the spleen off the diaphragm
![Dissecting the spleen off the diaphragm]()
Soundsettings The video clip can be played back with the automatic soundtrack of the subtitles.
In the sidebar registered users can enable and disable the automatic start of the dubbing.
Remark: Since this is a text-to-speech computer voice, it may mispronounce some medical terminology.Now transect the suspensory ligaments tying the spleen to the diaphragm, which then allows en blocmobilization of the spleen and pancreatic tail.
Under gentle traction first mobilize the spleen and then the pancreatic tail step by step mediad. .
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$87.34/ yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$174.70 / yearly payment