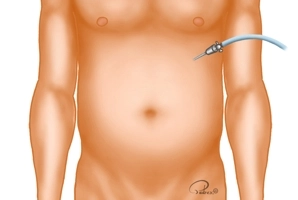
A small skin incision is made at the lower edge of the left costal arch near the xiphoid. Through this, the Veress needle is introduced, and the pneumoperitoneum is established. The pressure plateau is limited to 12mmHg.
Alternatively, the Veress needle can be introduced through an approximately 1 cm long periumbilical skin incision, and the pneumoperitoneum established through this, or the primary trocar access with the establishment of the pneumoperitoneum in an open technique can be chosen.
-
Creation of the capnoperitoneum
![Creation of the capnoperitoneum]()
Soundsettings -
Trocar positioning
![Trocar positioning]()
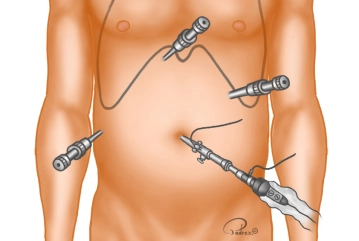
Soundsettings The channel for the optical trocar (10 mm) is bluntly pre-prepared with closed scissors after a small incision in the navel before its placement. The patient is placed in the anti-Trendelenburg position and the table is tilted slightly to the left, resulting in better exposure of Calot's triangle. Subsequently, the abdominal cavity is inspected. Then, under direct vision, the three additional trocars are placed in the following order:
Subxiphoidal right of the midline 5 mm working trocar (T2), left medioclavicular (above the navel) 10 mm working trocar (T3), right anterior axillary line (below the costal margin) 5 mm working trocar (T4)Tip: To avoid cosmetically noticeable 10 mm incisions, the umbilical incision can be made directly in the navel area and the trocar in the left mid-abdomen can be reduced to 5 mm when using a 5 mm camera.
-
Exposure of the gallbladder
![Exposure of the gallbladder]()
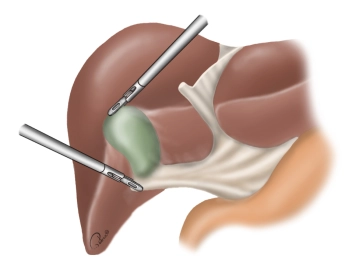
Soundsettings The gallbladder is grasped at the fundus (grasping forceps over T2) and luxated cranially over the liver. With a second grasping forceps (over T4), the infundibulum is grasped and pulled laterally. This stretches the Calot's triangle.
Note: In the case presented here, there is an acute cholecystitis with a significantly thickened, partially hemorrhagic wall and beginning inflammatory pannus formation in Calot's triangle.
-
Preparation of Calot's Triangle
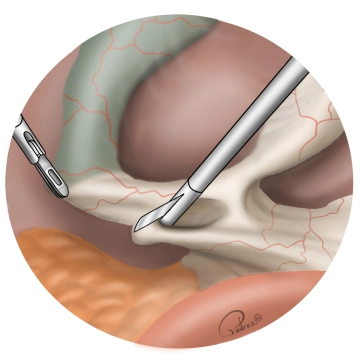
After blunt dissection of the cystic duct, its course (from the infundibulum of the gallbladder to
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$87.98/ yearly payment
general and visceral surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$176.00 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.