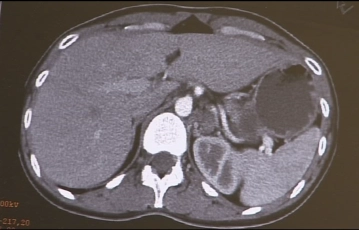
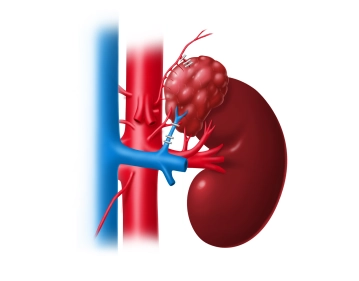
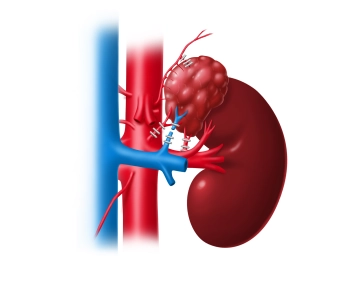
The imaging shows an approximately 5-6 cm large, multinodular, cystic-appearing mass in the region of the left adrenal gland, which has been clinically identified as a pheochromocytoma.
-
Computed Tomography Findings
![Computed Tomography Findings]()
-
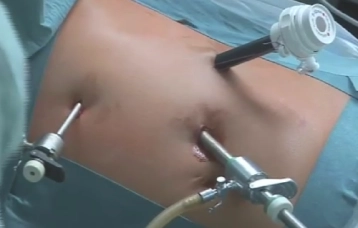
Trocar Positioning
![Trocar Positioning]()
Establishment of the capnoperitoneum after a 2 cm long minilaparotomy in the left middle upper abdomen as access for the optical trocar. After inspection of the abdominal cavity, insertion of two additional working trocars, 5 mm in the left epigastrium and a 12 mm trocar ventral to the left 11th rib.
-
Mobilization of the descending colon
-
Opening of the prerenal space
-
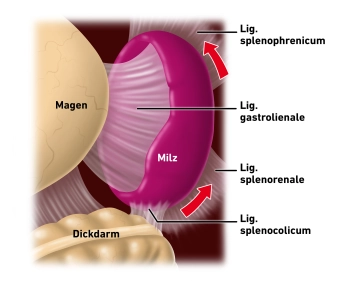
Detachment of the spleen from the diaphragm
-
Exposure of the left upper retroperitoneal space
-
Access to the Adrenal Gland
![Access to the Adrenal Gland]()
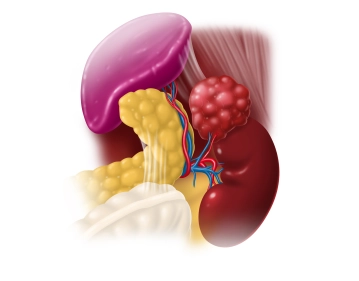
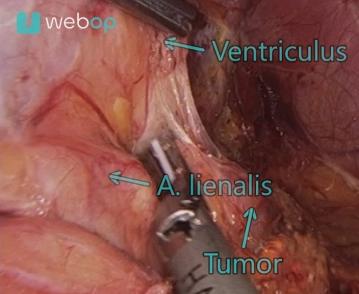
Soundsettings After careful cranially directed lifting of the pancreatic tail, one finds at its end dorsal to the spleen or the adjacent stomach wall the access to the adrenal gland. Now begins the exposure initially from lateral under careful transection of the small, predominantly venous vascular connections. This is performed with the ultrasonic scalpel, thereby exposing the lateral esophageal hiatus and the left crus of the diaphragm.
-
Mobilization of the Adrenal Tumor
![Mobilization of the Adrenal Tumor]()
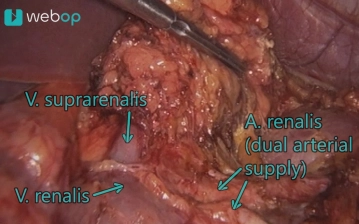
Soundsettings Exposure of the adrenal gland from medial. The medial boundary of the adrenal tumor can be displayed ventral to the aorta. The lower edge borders on the renal vein. During the now successive dissection from caudal to cranial, an arterial double supply with a lower and upper renal artery is revealed. This preparation is also performed with the ultrasonic scissors.
Note: 18 % of all patients have more than one renal artery per side (accessory vessels). -
Division of the central adrenal vein
![Division of the central adrenal vein]()
Soundsettings First, division of the superior suprarenal artery, which arises from the inferior phrenic artery, between clips. Then, the renal vein is exposed. The adrenal vein typically leaves the adrenal gland on the anterior surface and crosses the renal artery. The adrenal vein is clipped close to the tumor with 3 titanium clips and divided between the 2nd and 3rd clip.
-
Interruption of the arterial supply
-
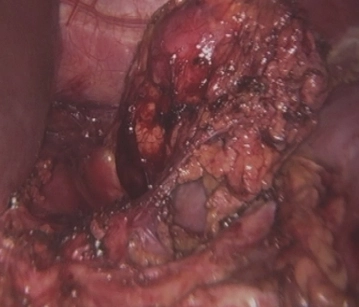
Total extirpation of the adrenal gland
-
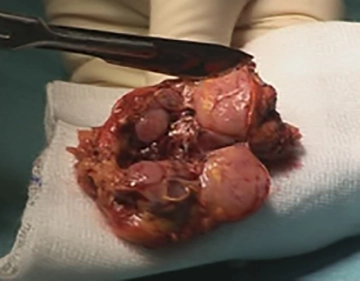
Removal of the Specimen, Drainage
![Removal of the Specimen, Drainage]()
Soundsettings After checking for hemostasis, the adrenal tumor can be removed in the retrieval bag.
The unchanged residual adrenal gland attached to the tumor is recognized.
After cutting open the specimen, multiple medullary tumors of different sizes are revealed.
Insertion of an Easyflow drainage. Finally, careful repositioning of the dislocated spleen. -
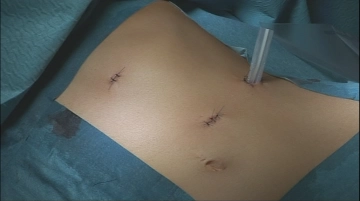
Wound closure
![Wound closure]()
After removal of the trocars, closure of the incisions using fascial and skin sutures. Suturing of the Easyflow drainage.