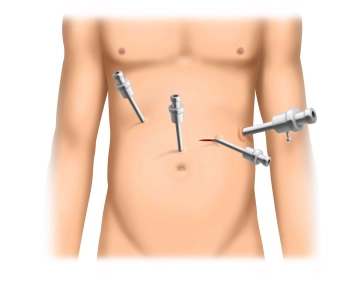
After a short incision in the left lateral mid-abdomen, access to the abdomen is achieved under visual control using a 12mm disposable trocar with optical function.
Subsequently, three 5mm trocars are inserted in an arc shape above the umbilical level into the upper or mid-abdomen. An additional 5mm trocar (as in the example) can optionally be placed high epigastrically.
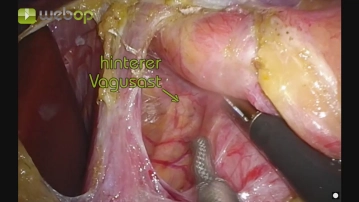
With a fan-shaped retractor, the left liver lobe is elevated, making the gastroesophageal junction accessible.