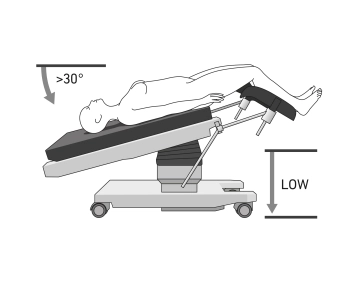
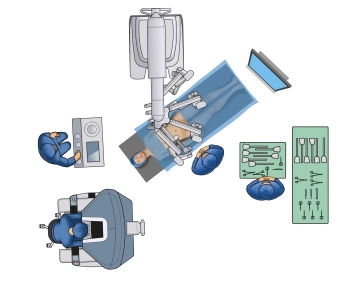
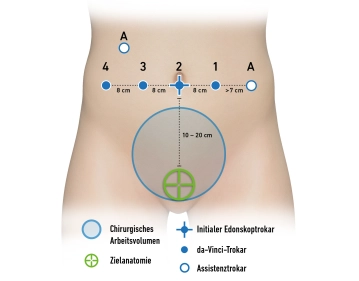
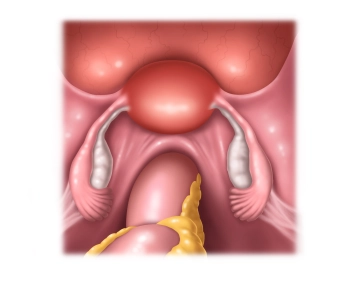
- Positioning is done in lithotomy position (or more safely on abductable straight leg supports), ideally on a large vacuum cushion or non-slip mat
- It is recommended to position both arms (caution: cotton wrapping when positioning with a cloth sling), or to position one arm on the side of the robot
- For leg positioning, padded "boots" are recommended so that the legs can be moved separately and covered sterilely if needed. Alternatively, the legs can be positioned in leg holders with fixation of the legs in them (Caution: compartment syndrome).
- The legs should be adjustable via the OR table control during the procedure
- Shoulder supports bilaterally to prevent the patient from slipping on the OR table
- For longer procedures, application of pneumatic compression cuffs for the legs for thrombosis prophylaxis
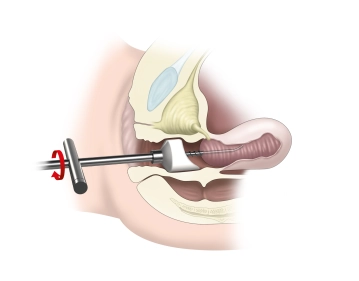
- Attachment of a cervical adapter
Note: It is important to consider the risk of injury to the patient from the instruments if the patient slips. With coupled tables in the Xi system, intraoperative position changes are possible without uncoupling. If the "Table-Motion" technique is not available, the surgical robot must always be undocked and removed from the OR table before any position change