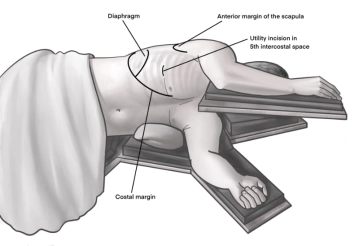
Incision of approximately 4 cm in length in the area of the anterior axillary line at the upper edge of the 5th rib to access the 4th intercostal space above. A helpful orientation is often an imaginary line from the tip of the scapula to the nipple. Transection of the subcutaneous tissue on the rib with the monopolar knife. Subsequently, stepwise preparation of the intercostal musculature with the monopolar knife. The pleura is opened bluntly with a finger. Palpation of the thoracic wall for adhesions and insertion of a wound protection film.
-
Access uniportal VATS right
![Access uniportal VATS right]()
-
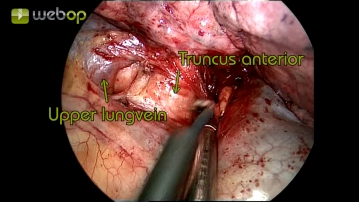
Preparation of the lung hilum
![Preparation of the lung hilum]()
Soundsettings First, the exploration of the thorax and the release of minor adhesions follows. Subsequently, the exposure of the lung hilum begins with incision and blunt dissection of the pleural covering, and exposure of the anterior trunk of the right pulmonary artery and the upper pulmonary vein.
-
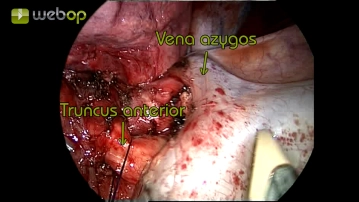
Resection of the anterior trunk
-
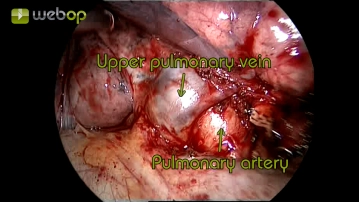
Preparation of the superior pulmonary vein
Dissection of the minor fissure (between the upper and middle lobes)
By visualizing the superior pulmonary vein, the pulmonary artery, and the entry of the middle lobe
By visualizing the superior pulmonary vein, the pulmonary artery, and the entry of the middle lobe
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
US$9.40
inclusive VAT
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
from US$4.35 / module
US$52.30/ yearly payment
thoracic
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$8.71
/ month
US$104.60 / yearly payment