Origin
- From the thoracic aorta after its passage through the aortic hiatus in the diaphragm at the level of T12
Course
- Retroperitoneal
- Left to the median plane and anterior to the spine
- Bifurcation into the common iliac arteries (bifurcatio aortae) at the level of the umbilicus / L4
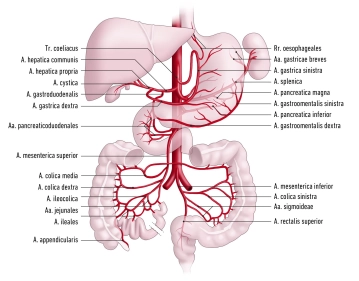
Branches from superior to inferior
- Inferior phrenic artery, left and right
- Celiac trunk
- Middle suprarenal artery, left and right
- Superior mesenteric artery
- Renal artery, left and right
- Ovarian / testicular artery, left and right
- Lumbar arteries
- Inferior mesenteric artery
- Median sacral artery
Distribution
- Paired branches: Abdominal wall, paired retroperitoneal organs, gonads
- Unpaired branches: Spleen, unpaired intestinal organs