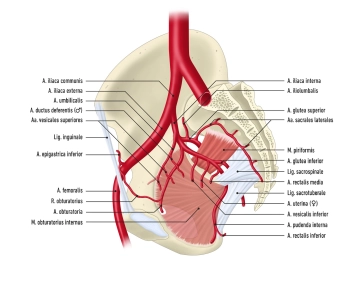
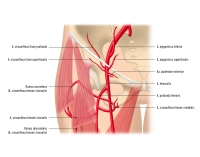
- The abdominal aorta divides at the aortic bifurcation (approximately at the level of L4) into the two common iliac arteries
- each common iliac artery in turn divides into an internal and external iliac artery
- The internal iliac artery supplies mainly the pelvic viscera with visceral branches, and with its parietal branches it is involved in the supply of the lower extremities
- The external iliac artery contributes to the supply of the pelvis and becomes the femoral artery after passing through the vascular lacuna
1. Internal Iliac Artery
Origin |
|
|---|---|
Course |
|
Positional Relationships |
|
Branches | visceral branches:
parietal branches:
|
Supply Area |
|
1.1 Visceral Branches of the Internal Iliac Artery
Main Branches | Course and Branches | Supply Area |
|---|---|---|
Umbilical Artery |
|
|
Inferior Vesical Artery |
|
|
Middle Rectal Artery |
|
|
Uterine Artery (Women) |
|
|
1.2 Parietal Branches of the Internal Iliac Artery
Main Branches | Course and Branches | Supply Area |
|---|---|---|
Iliolumbar Artery |
|
|
Lateral Sacral Arteries |
|
|
Superior Gluteal Artery |
|
|
Inferior Gluteal Artery |
|
|
Obturator Artery |
|
|
Internal Pudendal Artery |
|
|
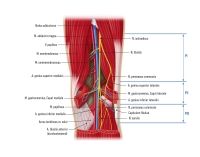
2. External Iliac Artery
Origin |
|
|---|---|
Course |
|
Positional Relationships |
|
Branches |
|
Supply Area |
|