The consensus document TASC II (Transatlantic Inter-Society Consensus for the Management of Peripheral Arterial Disease) deals with aspects of revascularization in PAD.
According to the TASC criteria, therapeutic treatment options can be derived depending on the local occlusion/stenosis length. The length of the stenosis and its localization regions decide on the therapy: endovascular or open vascular surgery.
TASC criteria for femoropopliteal vascular occlusions
Types | Morphology | Therapy principle |
|---|---|---|
A | Single stenosis <5 cm length, not at the origin of the SFA or in distal popliteal artery, single occlusion <3 cm length (not at the origin of the SFA or popliteal artery) | endovascular |
B | Single stenosis 5–10 cm length, not in distal popliteal artery, single occlusion 3–10 cm length, not in distal popliteal artery, calcified stenosis <5 cm length, multiple lesions <3 cm length | endovascular |
C | Single occlusion 3–10 cm length up to distal popliteal artery, multiple focal lesions 3–5 cm length without/with calcification, single stenosis/occlusion >10 cm length | open reconstruction |
D | Complete occlusion of CFA and/or SFA, complete occlusion of popliteal artery and trifurcation, severe diffuse disease | open reconstruction |
Video example: TASC C → open reconstruction
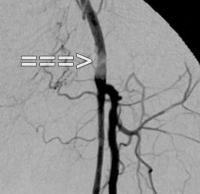
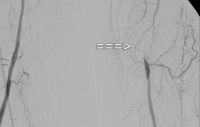
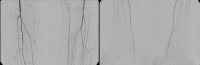
PAD stage IIb left (walking distance under 100 m). The preoperative DSA shows:
- a subtotal stenosis of the common femoral artery
- a long-segment occlusion of the superficial femoral artery in the adductor canal
- partial occlusions of the lower leg arteries