Carry the longitudinal inciison along the anterior margin of the left sternocleidomastoid muscle. Divide the subcutaneous tissue and platysma, perform subtle hemostasis, ligature, and divide the lateral capsular vein of the thyroid gland.
-
Left cervical access
-
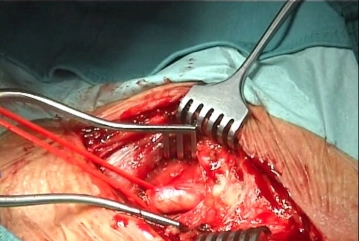
Dissecting the left common carotid artery
![Dissecting the left common carotid artery]()
Soundsettings Central exposure of the anterior aspect of the common carotid artery (CCA), which is then freed circumferentially; encircle it with a vessel loop as tourniquet. Continue the dissection cephalad mobilizing and medializing the cervical ansa. Dissect the facial vein and divide it between suture ligatures.
Tips:
1. Golden rule for dissection: Because of the risk of embolization, dissect the surrounding tissue off the CCA, not the other way around. The vessel should be handled as little as possible when dissecting.
2. The ansa cervicalis is the landmark leading straight to the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII). If dissection is approached differently, as in the video, problems will arise at the level of the internal carotid artery at the latest: The latter must then be subsequently medialized, which not only wastes time but also increases the risk of accidental injury to the hypoglossal nerve.
3. The facial vein should not be secured with simple ligatures, but always with suture ligatures. During emergence from anesthesia and also during coughing, the cervical veins are subjected to high pressures, which can cause simple ligatures to slip off, resulting in intense bleeding.
Mobilize the hypoglossal nerve and ansa cervicalis by transecting between clips small, vascular bra
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$52.55/ yearly payment
vascular surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$105.10 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.