Origin |
|
Course |
|
Division |
|
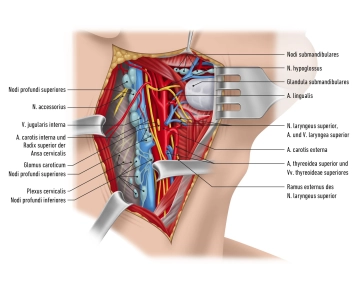
Distribution | 1. Internal carotid artery
2. External carotid artery
|
-
Common carotid artery
![Common carotid artery]()
Zum Vergrößern bitte anklicken -
Internal carotid artery
Origin
- Branch of the common carotid artery (carotid bifurcation)
Caudocephalad course
1. Cervical part
- Segment between origin of common carotid artery and base of skull
- Enters the skull via the carotid canal
- Does not give rise to any branches
2. Petrous part
- Courses in the petrous portion of the temporal bone
- Minor branches to the tympanic cavity and pterygoid canal
3. Cerebral part
- Courses in the subarachnoid space
- Passes through the dura mater
- Divides into anterior and middle cerebral artery
- Anterior cerebral artery communicates via the anterior communicating artery with the contralateral anterior cerebral artery
The arterial vascular ring at the base of the brain supplying it with blood is known as the cerebral arterial circle (of Willis). From anterior to posterior, it comprises the following vessels:
- Anterior communicating artery (unpaired)
- Anterior cerebral artery (left and right)
- Internal carotid artery (left and right) and its direct continuation, the middle cerebral artery
- Posterior communicating artery (left and right)
- Posterior cerebral artery (left and right, both arising from the basilar artery).
However, the circle of Willis has numerous variations both in branch caliber and anastomoses (hypoplasia of individual branches or even agenesis of subsegments). This is clinically relevant for collateral blood supply in stenosis.
-
External carotid artery
The areas supplied by the external carotid artery can be divided into four groups depending on their location: anterior, middle and posterior group and the terminal branches.
1. Anterior group
Branches (cranial -→ caudal)
Branches
Area supplied
Thyroid artery
- Infrahyoid branch
- Cricothyreoid branch
- Sternocleidomastoid branch
- Homonymous muscles
- Superior laryngeal artery
- Inner larynx
- Glandular branches
- Thyroid gland
Lingual artery
- Suprahyoid branch
- Hyoid bone
- Dorsal lingual branches
- Dorsum of tongue
- Sublingual artery
- Sublingual gland
- Deep lingual artery
- Tip of tongue
Facial artery
- Ascending palatine artery
- Soft palate
- Tonsils
- Pharynx
- Submental artery
- Submandibular gland
- Suprahyoid muscles
- Inferior labial artery
- Lower lip
- Superior labial artery
- Upper lip
- Angular artery
- Medial canthus
2. Middle group
Branches (cranial -→ caudal)
Branches
Area supplied
Ascending pharyngeal artery
- Pharyngeal branches
- Pharynx
- Inferior tympanic artery
- Tympanic cavity
- Posterior meningeal artery
- Dura mater
3. Posterior group
Branches (cranial -→ caudal)
Branches
Area supplied
Occipital artery
- Mastoid branch
- Mastoid cells
- Occipital branches
- Occipital region
- Meningeal branch
- Dura mater
Posterior auricular artery
- Auricular branch
- External ear
- Occipital branch
- Occipital region
- Stylomastoid artery
- Facial nerve
- Tympanic cavity
- Mastoid cells
- Posterior tympanic arteries
- Tympanic cavity
- Mastoid cells
- Pharyngeal branches
- Pharynx
- Parotid branch
- Parotid gland
- Parotid branch
- Parotid gland
4. Terminal branches
Branches (cranial -→ caudal)
Area supplied
Superficial temporal artery
- Transverse facial artery
- Face
- Zygomatico-orbital artery
- Lateral canthus
- Middle temporal artery
- Temporalis muscle
- Frontal branch
- Scalp
Maxillary artery
Mandibular part
- Deep auricular artery
- Temporomandibular joint
- External acoustic meatus
- Anterior tympanic artery
- Tympanic cavity
- Inferior alveolar artery
- Teeth
- Mandibula
- Mylohyoid branch: floor of mouth
- Mental branch: chin
- Middle meningeal artery
- Meninges
Pterygoid part
- Masseteric artery
- Masseter muscle
- Pterygoid branches
- Pterygoid muscles
- Deep temporal arteries
- Temporalis muscle
- Buccal artery
- Buccinator muscle
Pterygopalatine part
- Posterior superior alveolar artery
- Teeth
- Maxilla
- Infraorbital artery
- Maxilla
- Descending palatine artery
- Tonsils
- Soft palate
- Sphenopalatine artery
- Nasal cavity
- Nasal septum
- Artery of pterygoid canal
- Pharynx
- Tympanic cavity
The superficial and deep venous systems join in the venous (Pirogoff) angulus to become the brachio
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$52.55/ yearly payment
vascular surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$105.10 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.