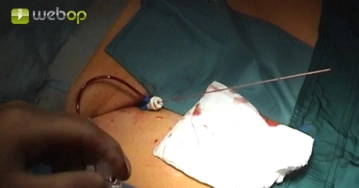
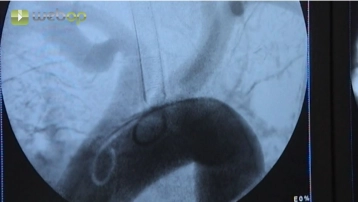
Puncture the right femoral artery in Seldinger technique at the groin and carefully introduce the guidewire. Remove the puncture cannula and introduce a 6F or 7F sheath under fluoroscopic guidance. Remove the guidewire and check the pulsatile return flow and then administer locally 5000 IU of heparin saline solution. Under fluoroscopic guidance, advance a long Terumo® guidewire through the right iliac axis into the aorta.
Tips:
1. Do not exert force when puncturing the femoral artery because of the risk of inguinal vascular dissection.
2. If percutaneous puncture via both groins fails, make a mini-incision in one groin, expose the common femoral artery there and then puncture under direct vision. Access via puncture of the contralateral arm is possible, but probing will become much more difficult.