Overview
Origin |
|
|---|---|
Course |
|
Branches |
|
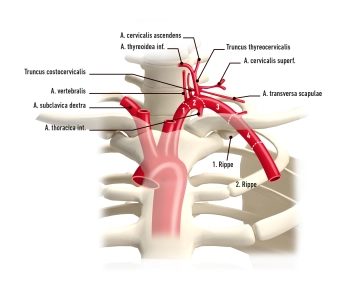
Main branches of the subclavian artery and supply area
Main branches (proximal → distal) | important branches (proximal → distal) | Supply area |
|---|---|---|
Internal thoracic artery | Ø |
|
Vertebral artery | Ø |
|
Thyrocervical trunk | Suprascapular artery |
|
Transverse cervical artery → Dorsal scapular artery |
| |
Ascending cervical artery |
| |
Inferior thyroid artery |
| |
Costocervical trunk | Deep cervical artery |
|
Supreme intercostal artery |
|
According to vascular surgical criteria, the course of the subclavian artery is divided into four sections:
Section | Characteristic |
|---|---|
A1 | Aortic arch to origin of vertebral artery (VA) |
A2 | VA to thyrocervical trunk (TT) |
A3 | TT to crossing of 1st rib |
A4 | Crossing of 1st rib to exit under clavicle, here beginning of axillary artery |