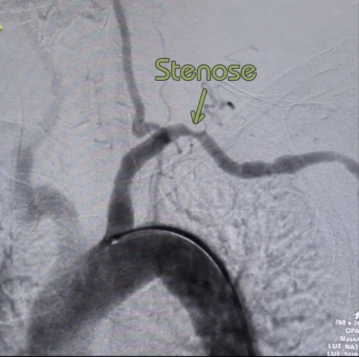
Stenosis or occlusion of the subclavian artery only in cases of clearly attributable symptoms/hypoperfusion of the arm:
- claudication-like arm complaints (load-dependent ischemia)
- acral lesions in the finger area
- Subclavian Steal Syndrome
Classification of arterial occlusive disease of the upper extremity based on the Fontaine classification of the lower extremity |
|---|
Stage I | asymptomatic stenosis/occlusion |
|---|---|
Stage II | load-dependent fatigue, weakness or pain in the affected arm |
Stage III | constant pain symptoms, nocturnal rest pain |
Stage IV | trophic disorders, necrosis formation in the acral area |