- Positioning: Supine position with legs spread on a vacuum cushion. The cushion ensures stability, reducing the need for additional supports
- After trocar placement, the table is tilted to a 15° – 30° Anti-Trendelenburg position to optimize access
- Robot Docking:
- The Xi system offers flexibility in the docking position, typically from the left
- For X or Si systems, the cart is docked cranially from the right
- Team Positioning:
- Surgeon: At the console, ideally with a view of the patient and assistant
- Assistant: Positioned between the legs, sitting or standing
- Scrub Nurse: On the right side of the patient
- Anesthesiologist: At the patient’s head, on the right side
-
Patient Positioning and Operating Room Setup
-
Pneumoperitoneum, Trocar Placement, and Docking
![Pneumoperitoneum, Trocar Placement, and Docking 1]()
![511_Trokarpositionen.jpeg]()
![Pneumoperitoneum, Trocar Placement, and Docking 3]()
Soundsettings Pneumoperitoneum Creation:
- Use a Veress needle at the Palmer point in the left upper abdomen.
- Establish an insufflation pressure of 12–15 mmHg
- Alternatively, employ Optiview technique
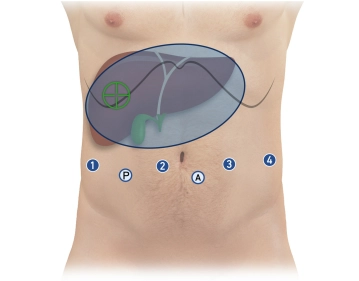
Trocar Placement:
- Total Ports:
- Four 8 mm robotic ports in a linear arrangement, 15–20 cm from the target anatomy (infraumbilical)
- Two 12 mm laparoscopic ports:
- Assistant trocar (caudal between robotic ports 2 and 3)
- Pringle maneuver trocar (caudal between robotic ports 1 and 2)
- Spacing: Approximately 8 cm between each port
- Position robotic trocars at the level of the muscular abdominal wall (aligning the broad black ring, the “Remote Center”)
Initial Instrument Configuration:
- Robotic ports (from right to left):
- Port 1: Monopolar curved scissors
- Port 2: Camera
- Port 3: Bipolar forceps
- Port 4: Prograsp forceps
Docking the Robot:
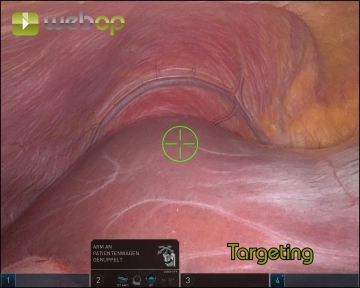
- Dock the camera arm first (port 2)
- Execute Targeting (Xi system) to align robot arms with the surgical target
- Dock the remaining arms, ensuring 1 fist-width spacing between them
- Insert instruments under direct visualization via the assistant trocar
Key Precautions and Tips
Trocar Stability:
- Ensure the “Remote Center” aligns with the muscular abdominal wall to minimize shear forces during instrument movement
Instrument Placement:
- Use the assistant trocar and camera to inspect trocar alignment and verify instrument positioning before proceeding
Preventing Patient Movement:
- Double-check the vacuum cushion for leaks before sterile draping
- Secure arms during docking to avoid injury if the patient shifts
Control Checks:
- Before docking:
- Mark trocar points and ensure proper spacing
- Introduce the camera manually for inspection
- After docking:
- Verify arm alignment and positioning of instruments
-
Pre-Docking Checklist
- Perform a small incision in the left upper abdomen for Veress needle placement
- Establish pneumoperitoneum at 15 mmHg
- Mark the trocar line and insert the first robotic trocar
- Insert the camera manually to confirm placement
- Sequentially place:
- Three additional robotic trocars (8 mm)
- Two laparoscopic trocars (12 mm) in the caudal positions
- Transition to Anti-Trendelenburg position (15°)
- Dock the camera arm and insert the camera
- Perform Targeting with the Xi system
- Dock the remaining three arms
- Insert instruments and park them at the target anatomy:
- Port 1: Monopolar curved scissors
- Port 2: Camera
- Port 3: Bipolar forceps
- Port 4: Prograsp forceps
- Inspect remote centers via the assistant trocar to ensure proper alignment
This systematic approach optimizes patient safety, instrument positioning, and robot utilization, ensuring precision in robotic-assisted right hemihepatectomy.
-
Intraoperative Sonography and Marking the Resection Line
![Intraoperative Sonography and Marking the Resection Line]()
Soundsettings Adhesiolysis:
- Release adhesions between the omentum majus, gallbladder, and inferior liver surface
- Grasp the gallbladder fundus with the Prograsp Forceps and retract cranially
- Expose the entire gallbladder to the infundibulum
Intraoperative Ultrasound:
- Insert the ultrasound probe through the assistant trocar
- Guide the probe with fenestrated bipolar forceps for precise movement
- Objective:
- Visualize lesions and their relationship to vessels and bile ducts
- Confirm the tumor-free status of the left liver lobe
- Identify critical landmarks, including the middle hepatic vein and segmental branches to Segments V/VI and VIII
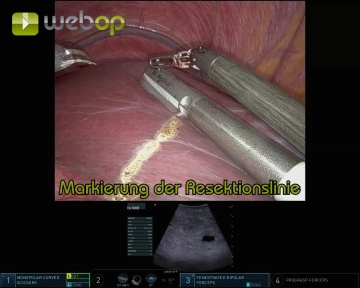
Marking the Resection Line:
- Using monopolar scissors, mark the resection line on the ventral liver capsule under ultrasound guidance
-
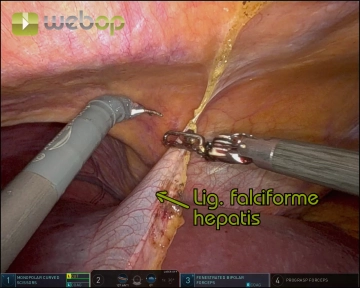
Division of the Ligamentum teres and Ligamentum falciforme hepatis
![Division of the Ligamentum teres and Ligamentum falciforme hepatis]()
Soundsettings Create a window between the ligamentum teres and the abdominal wall
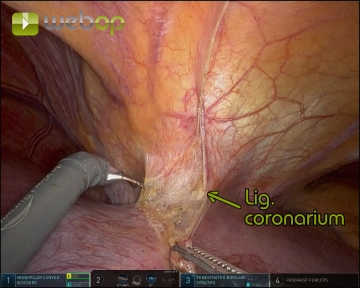
Gradually divide both ligaments with meticulous coagulation, progressing from caudal to cranial up to the diaphragm and coronary ligament
- Tip: Use the detached ligamentum teres as a traction point for atraumatic manipulation of the liver during the procedure
-
Exposure of the suprahepatic inferior vena cava
Access and Exposure:Elevate the liver using the Prograsp Forceps on the ligamentum teresOpen the om
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$52.55/ yearly payment
robotics
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$105.10 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.