Origin |
|
|---|---|
Course |
|
Division |
|
Vascular territory | 1. Internal carotid artery
2. External carotid artery
|
-
A. carotis communis
![A. carotis communis]()
Zum Vergrößern bitte anklicken -
Subclavian artery
Origin
- left from the aortic arch
- right from the brachiocephalic trunk
Course
- passes over the pleural dome between clavicle and 1st rib through the posterior scalene gap (between M. scalenus anterior and M. scalenus medius)
Branches
- internal thoracic artery
- vertebral artery
- thyrocervical trunk
- costocervical trunk
Main branches of the subclavian artery
Branches
Branches
Supply area
internal thoracic artery
Ø
- anterior thoracic wall
- upper abdominal wall
- mediastinum
- pericardium
- diaphragm
vertebral artery
Ø
- brain
- cervical spine (vertebrae, spinal cord)
- deep neck musculature
thyrocervical trunk
- suprascapular artery
- anastomosis with branches of the axillary artery
- transverse cervical artery -> dorsal scapular artery
- musculature of neck, nape, shoulder
- ascending cervical artery
- neck musculature
- inferior thyroid artery
- trachea
- larynx
- thyroid gland
- esophagus
costocervical trunk
- deep cervical artery
- deep neck musculature
- supreme intercostal artery
- upper intercostal muscles
After passing through the posterior scalene gap, the subclavian artery transitions into the axillary artery. This supplies the shoulder girdle and then becomes the brachial artery, whose supply area is the upper arm. In the elbow crease, the brachial artery divides into the radial artery and ulnar artery, which run along the forearm to the hand. The arteries are accompanied by veins of the same name.
-
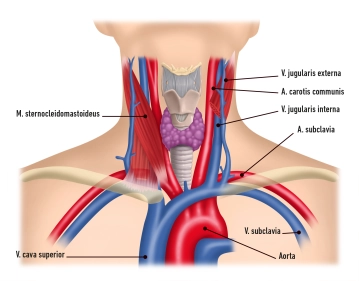
Venous System
Superficial and deep venous systems unite in the Angulus venosus ("venous angle") to form the V. brachiocephalica and empty into the V. cava superior.
1. Superficial Veins
V. jugularis externa
- runs in the lateral neck area covered by the Platysma
- penetrates the Lamina superficialis of the cervical fascia
- empties in the venous angle, possibly even earlier, into the V. jugularis interna, then into the V. cava superior
V. jugularis anterior
- usually runs over the M. sternocleidomastoideus
- Vv. jugulares anteriores of both sides usually unite in the Spatium suprasternale to form the Arcus venosus jugularis
- empties into venous angle or into the V. jugularis externa
2. Deep Veins
V. jugularis interna
- see below
V. subclavia
- Continuation of the V. axillaris
- runs in front of the M. scalenus anterior
- empties in the venous angle together with the V. jugularis interna and forms the V. brachiocephalica → V. cava superior
The lymphatic drainage of the head and neck empties into the paired jugular trunks.Left Jugular Tru
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$52.30/ yearly payment
vascular surgery
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$104.60 / yearly payment
Webop is committed to education. That's why we offer all our content at a fair student rate.