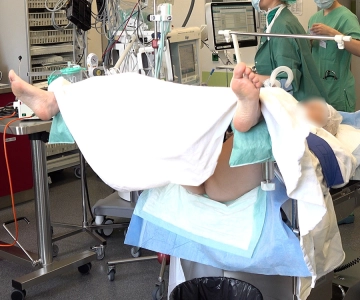
The positioning of the patient during hysteroscopy is in the lithotomy position using leg holders. The patient lies on her back, and her legs are bent at the hip joints at approximately 90°. The knees are also significantly bent. The lower legs are positioned on the leg holders so that the legs are slightly spread apart. This arrangement allows optimal access to the vaginal and uterine area for the procedure.
-
Positioning
![Positioning]()
-
Examination under Anesthesia
Soundsettings After positioning, catheterization of the bladder is performed to ensure bladder emptying. Subsequently, a speculum examination is conducted to visualize the cervix. Additionally, a bimanual and rectovaginal examination is performed to assess the anatomical conditions of the pelvis and to detect possible infiltrations.
-
Pap smear
-
Colposcopy with acetic acid test and Schiller's iodine test
Soundsettings Colposcopy is performed with the application of acetic acid to the cervix to make abnormal cellular changes more visible. The acetic acid test results in a reversible protein denaturation in dysplastic or neoplastic epithelial cells, causing them to appear whitish (known as acetowhite staining). This reaction occurs particularly in high-grade dysplasias and facilitates the identification of pathological areas.
Additionally, the Schiller's iodine test is conducted, where an iodine solution is applied to the cervix. Healthy cells containing glycogen stain brown, while pathologically altered or glycogen-poor areas remain colorless (or yellow). In particular, dysplastic tissue, HPV-induced lesions, or precancerous conditions appear iodine-negative and can thus be more precisely localized.
Conization is typically performed using a LEEP loop (Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure). An e
Activate now and continue learning straight away.
Single Access
Activation of this course for 3 days.
Most popular offer
webop - Savings Flex
Combine our learning modules flexibly and save up to 50%.
US$52.30/ yearly payment
gynecology
Unlock all courses in this module.
US$104.60 / yearly payment